9. Greedy 활용
- 1. 씨름 선수
- 2. 회의실 배정
- 3. 결혼식
- 4. 최대 수입 스케쥴(PriorityQueue 응용문제)
- 5. 다익스트라 알고리즘
- 6. 친구인가? (Disjoint-Set : Union&Find)
- 7. 원더랜드(최소스패닝트리 : 크루스칼, Union&Find 활용)
- 8. 원더랜드(최소스패닝트리 : 프림, PriorintyQueue)
1. 씨름 선수
현수는 씨름 감독입니다. 현수는 씨름 선수를 선발공고를 냈고, N명의 지원자가 지원을 했습니다. 현수는 각 지원자의 키와 몸무게 정보를 알고 있습니다.
현수는 씨름 선수 선발 원칙을 다음과 같이 정했습니다.
“A라는 지원자를 다른 모든 지원자와 일대일 비교해서 키와 몸무게 모두 A지원자 보다 높은(크고, 무겁다) 지원자가 존재하면 A지원자는 탈락하고, 그렇지 않으면 선발된다.”
N명의 지원자가 주어지면 위의 선발원칙으로 최대 몇 명의 선수를 선발할 수 있는지 알아내는 프로그램을 작성하세요.
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에 지원자의 수 N(5<=N<=100,000)이 주어집니다.
두 번째 줄부터 N명의 키와 몸무게 정보가 차례로 주어집니다. 각 선수의 키와 몸무게는 모두 다릅니다.
▣ 출력설명
첫째 줄에 씨름 선수로 뽑히는 최대 인원을 출력하세요.
▣ 입력예제 1
5
172 67
183 65
180 70
170 72
181 60
▣ 출력예제 1
3
출력설명
(183, 65), (180, 70), (170, 72) 가 선발됩니다. (181, 60)은 (183, 65)보다 키와 몸무게 모두
낮기 때문에 탈락이고, (172, 67)은 (180, 70) 때문에 탈락입니다.
import java.util.*;
class Body implements Comparable<Body>{
public int h, w;
Body(int h, int w) {
this.h = h;
this.w = w;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Body o){
return o.h-this.h;
}
}
class Main {
public int solution(ArrayList<Body> arr, int n){
int cnt=0;
Collections.sort(arr);
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(Body ob : arr){
if(ob.w>max){
max=ob.w;
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<Body> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int h=kb.nextInt();
int w=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Body(h, w));
}
System.out.println(T.solution(arr, n));
}
}
2. 회의실 배정
한 개의 회의실이 있는데 이를 사용하고자 하는 n개의 회의들에 대하여 회의실 사용표를 만들려고 한다. 각 회의에 대해 시작시간과 끝나는 시간이 주어져 있고, 각 회의가 겹치지 않게 하면서 회의실을 사용할 수 있는 최대수의 회의를 찾아라. 단, 회의는 한번 시작하면 중간에 중단될 수 없으며 한 회의가 끝나는 것과 동시에 다음 회의가 시작될 수 있다.
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에 회의의 수 n(1<=n<=100,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 n+1 줄까지 각 회의의 정보가 주어지는데 이것은 공백을 사이에 두고 회의의 시작시간과 끝나는 시간이 주어진다.
회의 시간은 0시부터 시작된다.
회의의 시작시간과 끝나는 시간의 조건은 (시작시간 <= 끝나는 시간)입니다.
▣ 출력설명
첫째 줄에 최대 사용할 수 있는 회의 수를 출력하여라.
▣ 입력예제 1
5
1 4
2 3
3 5
4 6
5 7
▣ 출력예제 1
3
예제설명
(2, 3), (3, 5), (5, 7)이 회의실을 이용할 수 있다.
▣ 입력예제 2
3
3 3
1 3
2 3
▣ 출력예제 2
2
import java.util.*;
class Time implements Comparable<Time>{
public int s, e;
Time(int s, int e) {
this.s = s;
this.e = e;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Time o){
if(this.e==o.e) return this.s-o.s;
else return this.e-o.e;
}
}
class Main {
public int solution(ArrayList<Time> arr, int n){
int cnt=0;
Collections.sort(arr);
int et=0;
for(Time ob : arr){
if(ob.s>=et){
cnt++;
et=ob.e;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<Time> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int x=kb.nextInt();
int y=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Time(x, y));
}
System.out.println(T.solution(arr, n));
}
}
3. 결혼식
현수는 다음 달에 결혼을 합니다.
현수는 결혼식 피로연을 장소를 빌려 3일간 쉬지 않고 하려고 합니다.
피로연에 참석하는 친구들 N명의 참석하는 시간정보를 현수는 친구들에게 미리 요구했습니다.
각 친구들은 자신이 몇 시에 도착해서 몇 시에 떠날 것인지 현수에게 알려주었습니다.
현수는 이 정보를 바탕으로 피로연 장소에 동시에 존재하는 최대 인원수를 구하여 그 인원을 수용할 수 있는 장소를 빌리려고 합니다. 여러분이 현수를 도와주세요.
만약 한 친구가 오는 시간 13, 가는시간 15라면 이 친구는 13시 정각에 피로연 장에 존재하는 것이고 15시 정각에는 존재하지 않는다고 가정합니다.
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에 피로연에 참석할 인원수 N(5<=N<=100,000)이 주어집니다.
두 번째 줄부터 N줄에 걸쳐 각 인원의 오는 시간과 가는 시간이 주어집니다.
시간은 첫날 0시를 0으로 해서 마지막날 밤 12시를 72로 하는 타임라인으로 오는 시간과 가는 시간이 음이 아닌 정수로 표현됩니다.
▣ 출력설명
첫째 줄에 피로연장에 동시에 존재하는 최대 인원을 출력하세요.
▣ 입력예제 1
5
14 18
12 15
15 20
20 30
5 14
▣ 출력예제 1
2
import java.util.*;
class Time implements Comparable<Time>{
public int time;
public char state;
Time(int time, char state) {
this.time = time;
this.state = state;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Time ob){
if(this.time==ob.time) return this.state-ob.state;
else return this.time-ob.time;
}
}
class Main {
public int solution(ArrayList<Time> arr){
int answer=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Collections.sort(arr);
int cnt=0;
for(Time ob : arr){
if(ob.state=='s') cnt++;
else cnt--;
answer=Math.max(answer, cnt);
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<Time> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int sT=kb.nextInt();
int eT=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Time(sT, 's'));
arr.add(new Time(eT, 'e'));
}
System.out.println(T.solution(arr));
}
}
4. 최대 수입 스케쥴(PriorityQueue 응용문제)
현수는 유명한 강연자이다. N개이 기업에서 강연 요청을 해왔다. 각 기업은 D일 안에 와서 강연을 해 주면 M만큼의 강연료를 주기로 했다.
각 기업이 요청한 D와 M를 바탕으로 가장 많을 돈을 벌 수 있도록 강연 스케쥴을 짜야 한다.
단 강연의 특성상 현수는 하루에 하나의 기업에서만 강연을 할 수 있다.
▣ 입력설명
첫 번째 줄에 자연수 N(1<=N<=10,000)이 주어지고, 다음 N개의 줄에 M(1<=M<=10,000)과 D(1<=D<=10,000)가 차례로 주어진다.
▣ 출력설명
첫 번째 줄에 최대로 벌 수 있는 수입을 출력한다.
▣ 입력예제 1
6
50 2
20 1
40 2
60 3
30 3
30 1
▣ 출력예제 1
150
import java.util.*;
class Lecture implements Comparable<Lecture>{
public int money;
public int time;
Lecture(int money, int time) {
this.money = money;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Lecture ob){
return ob.time-this.time;
}
}
class Main {
static int n, max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int solution(ArrayList<Lecture> arr){
int answer=0;
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
Collections.sort(arr);
int j=0;
for(int i=max; i>=1; i--){
for(; j<n; j++){
if(arr.get(j).time<i) break;
pQ.offer(arr.get(j).money);
}
if(!pQ.isEmpty()) answer+=pQ.poll();
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<Lecture> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int m=kb.nextInt();
int d=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Lecture(m, d));
if(d>max) max=d;
}
System.out.println(T.solution(arr));
}
}
5. 다익스트라 알고리즘
아래의 가중치 방향그래프에서 1번 정점에서 모든 정점으로의 최소 거리비용을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하세요. (경로가 없으면 Impossible를 출력한다)
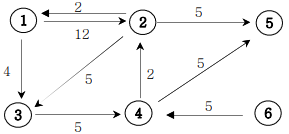
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에는 정점의 수 N(1<=N<=20)와 간선의 수 M가 주어진다. 그 다음부터 M줄에 걸쳐 연결정보와 거리비용이 주어진다.
▣ 출력설명
1번 정점에서 각 정점으로 가는 최소비용을 2번 정점부터 차례대로 출력하세요.
▣ 입력예제 1
6 9
1 2 12 // 1번 정점에서 2번정점으로 가는데 12의 비용이 든다.
1 3 4
2 1 2
2 3 5
2 5 5
3 4 5
4 2 2
4 5 5
6 4 5
▣ 출력예제 1
2 : 11
3 : 4
4 : 9
5 : 14
6 : impossible
import java.util.*;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
public int vex;
public int cost;
Edge(int vex, int cost) {
this.vex = vex;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge ob){
return this.cost-ob.cost;
}
}
class Main {
static int n, m;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> graph;
static int[] dis;
public void solution(int v){
PriorityQueue<Edge> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>();
pQ.offer(new Edge(v, 0));
dis[v]=0;
while(!pQ.isEmpty()){
Edge tmp=pQ.poll();
int now=tmp.vex;
int nowCost=tmp.cost;
if(nowCost>dis[now]) continue;
for(Edge ob : graph.get(now)){
if(dis[ob.vex]>nowCost+ob.cost){
dis[ob.vex]=nowCost+ob.cost;
pQ.offer(new Edge(ob.vex, nowCost+ob.cost));
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
n=kb.nextInt();
m=kb.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
dis=new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int a=kb.nextInt();
int b=kb.nextInt();
int c=kb.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Edge(b, c));
}
T.solution(1);
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++){
if(dis[i]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.println(i+" : "+dis[i]);
else System.out.println(i+" : impossible");
}
}
}
6. 친구인가? (Disjoint-Set : Union&Find)
오늘은 새 학기 새로운 반에서 처음 시작하는 날이다. 현수네 반 학생은 N명이다. 현수는 각학생들의 친구관계를 알고 싶다.
모든 학생은 1부터 N까지 번호가 부여되어 있고, 현수에게는 각각 두 명의 학생은 친구 관계가 번호로 표현된 숫자쌍이 주어진다. 만약 (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)의 숫자쌍이 주어지면 1번 학생과 2번 학생이 친구이고, 2번 학생과 3번 학생이 친구, 3번 학생과 4번 학생이 친구이다.
그리고 1번 학생과 4번 학생은 2번과 3번을 통해서 친구관계가 된다.
학생의 친구관계를 나타내는 숫자쌍이 주어지면 특정 두 명이 친구인지를 판별하는 프로그램을 작성하세요. 두 학생이 친구이면 “YES”이고, 아니면 ”NO”를 출력한다.
▣ 입력설명
첫 번째 줄에 반 학생수인 자연수 N(1<=N<=1,000)과 숫자쌍의 개수인 M(1<=M<=3,000)이주어지고, 다음 M개의 줄에 걸쳐 숫자쌍이 주어진다.
마지막 줄에는 두 학생이 친구인지 확인하는 숫자쌍이 주어진다.
▣ 출력설명
첫 번째 줄에 “YES”또는 “NO”를 출력한다.
▣ 입력예제 1
9 7
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 5
6 7
7 8
8 9
3 8
▣ 출력예제 1
NO
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int[] unf;
public static int Find(int v){
if(v==unf[v]) return v;
else return unf[v]=Find(unf[v]);
}
public static void Union(int a, int b){
int fa=Find(a);
int fb=Find(b);
if(fa!=fb) unf[fa]=fb;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
int m=kb.nextInt();
unf=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) unf[i]=i;
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){
int a=kb.nextInt();
int b=kb.nextInt();
Union(a, b);
}
int a=kb.nextInt();
int b=kb.nextInt();
int fa=Find(a);
int fb=Find(b);
if(fa==fb) System.out.println("YES");
else System.out.println("NO");
}
}
7. 원더랜드(최소스패닝트리 : 크루스칼, Union&Find 활용)
원더랜드에 문제가 생겼다. 원더랜드의 각 도로를 유지보수하는 재정이 바닥난 것이다.
원더랜드는 모든 도시를 서로 연결하면서 최소의 유지비용이 들도록 도로를 선택하고 나머지 도로는 폐쇄하려고 한다.
아래의 그림은 그 한 예를 설명하는 그림이다.
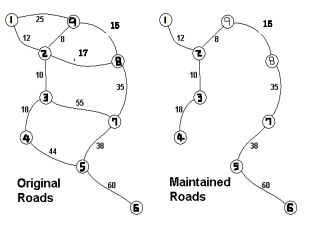
위의 지도는 각 도시가 1부터 9로 표현되었고, 지도의 오른쪽은 최소비용 196으로 모든 도시를 연결하는 방법을 찾아낸 것이다.
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에 도시의 개수 V(1≤V≤100)와 도로의 개수 E(1≤E≤1,000)가 주어진다. 다음 E개의 줄에는 각 도로에 대한 정보를 나타내는 세 정수 A, B, C가 주어진다. 이는 A번 도시와 B번 도시가 유지비용이 C인 도로로 연결되어 있다는 의미이다.
▣ 출력설명
모든 도시를 연결하면서 드는 최소비용을 출려한다.
▣ 입력예제 1
9 12
1 2 12
1 9 25
2 3 10
2 8 17
2 9 8
3 4 18
3 7 55
4 5 44
5 6 60
5 7 38
7 8 35
8 9 15
▣ 출력예제 1
196
import java.util.*;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
public int v1;
public int v2;
public int cost;
Edge(int v1, int v2, int cost) {
this.v1 = v1;
this.v2 = v2;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge ob){
return this.cost-ob.cost;
}
}
class Main {
static int[] unf;
public static int Find(int v){
if(v==unf[v]) return v;
else return unf[v]=Find(unf[v]);
}
public static void Union(int a, int b){
int fa=Find(a);
int fb=Find(b);
if(fa!=fb) unf[fa]=fb;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
int m=kb.nextInt();
unf=new int[n+1];
ArrayList<Edge> arr=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) unf[i]=i;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int a=kb.nextInt();
int b=kb.nextInt();
int c=kb.nextInt();
arr.add(new Edge(a, b, c));
}
int answer=0;
Collections.sort(arr);
for(Edge ob : arr){
int fv1=Find(ob.v1);
int fv2=Find(ob.v2);
if(fv1!=fv2){
answer+=ob.cost;
Union(ob.v1, ob.v2);
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
8. 원더랜드(최소스패닝트리 : 프림, PriorintyQueue)
원더랜드에 문제가 생겼다. 원더랜드의 각 도로를 유지보수하는 재정이 바닥난 것이다.
원더랜드는 모든 도시를 서로 연결하면서 최소의 유지비용이 들도록 도로를 선택하고 나머지 도로는 폐쇄하려고 한다.
아래의 그림은 그 한 예를 설명하는 그림이다.
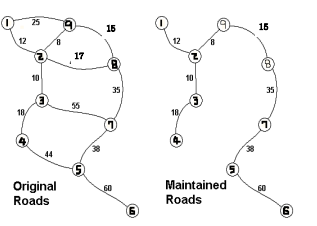
위의 지도는 각 도시가 1부터 9로 표현되었고, 지도의 오른쪽은 최소비용 196으로 모든 도시를 연결하는 방법을 찾아낸 것이다.
▣ 입력설명
첫째 줄에 도시의 개수 V(1≤V≤100)와 도로의 개수 E(1≤E≤1,000)가 주어진다. 다음 E개의 줄에는 각 도로에 대한 정보를 나타내는 세 정수 A, B, C가 주어진다. 이는 A번 도시와 B번 도시가 유지비용이 C인 도로로 연결되어 있다는 의미이다.
▣ 출력설명
모든 도시를 연결하면서 드는 최소비용을 출려한다.
▣ 입력예제 1
9 12
1 2 12
1 9 25
2 3 10
2 8 17
2 9 8
3 4 18
3 7 55
4 5 44
5 6 60
5 7 38
7 8 35
8 9 15
▣ 출력예제 1
196
import java.util.*;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
public int vex;
public int cost;
Edge(int vex, int cost) {
this.vex = vex;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge ob){
return this.cost-ob.cost;
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=kb.nextInt();
int m=kb.nextInt();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>>();
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<Edge>());
}
int[] ch=new int[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
int a=kb.nextInt();
int b=kb.nextInt();
int c=kb.nextInt();
graph.get(a).add(new Edge(b, c));
graph.get(b).add(new Edge(a, c));
}
int answer=0;
PriorityQueue<Edge> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>();
pQ.offer(new Edge(1, 0));
while(!pQ.isEmpty()){
Edge tmp=pQ.poll();
int ev=tmp.vex;
if(ch[ev]==0){
ch[ev]=1;
answer+=tmp.cost;
for(Edge ob : graph.get(ev)){
if(ch[ob.vex]==0) pQ.offer(new Edge(ob.vex, ob.cost));
}
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}