[멀티스레드와 동시성] 스레드 풀과 Executor 프레임워크2
- graceful shutdown
- ExecutorService 우아한 종료 - 구현
- Executor 스레드 풀 관리 - 코드
- Executor 스레드 풀 관리 - 분석
- Executor 전략
- 정리
graceful shutdown
애플리케이션이 종료될 때 현재 처리 중인 작업을 마무리하고 자원(스레드, 커넥션 등)을 정상적으로 해제한 후 종료되는 방식
ExecutorService의 종료 메서드
종료와 관련된 다양한 메서드를 설명한다
- 서비스 종료
void shutdown()- 새로운 작업을 받지 않고, 이미 제출된 작업을 모두 완료한 후에 종료한다.
- 논 블로킹 메서드(이 메서드를 호출한 스레드는 대기하지 않고 즉시 다음 코드를 호출한다.)
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()- 실행 중인 작업을 중단하고, 대기 중인 작업을 반환하며 즉시 종료한다. 실행 중인 작업을 중단하기 위해 인터럽트를 발생시킨다.
- 논 블로킹 메서드
- 서비스 상태 확인
boolean isShutdown()- 서비스가 종료되었는지 확인한다.
boolean isTerminated()shutdown(),shutdownNow()호출 후, 모든 작업이 완료되었는지 확인한다.
- 작업 완료 대기
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException- 서비스 종료시 모든 작업이 완료될 때까지 대기한다. 이때 지정된 시간까지만 대기한다.
- 블로킹 메서드
- close()
close()는 자바 19부터 지원하는 서비스 종료 메서드이다. 이 메서드는shutdown()과 같다고 생각하면 된다.- 더 정확히는
shutdown()을 호출하고, 작업이 완료되거나 인터럽트가 발생할 때 까지 무한정 반복 대기 한다. - 호출한 스레드에 인터럽트가 발생해도
shutdownNow()를 호출한다.
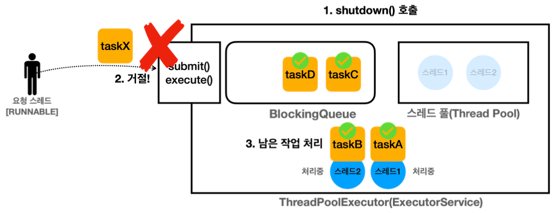
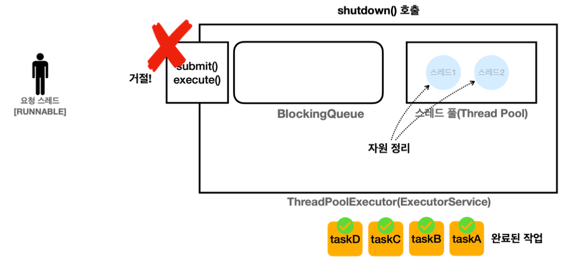
shutdown() - 처리중인 작업이 있는 경우
모든 작업을 완료하면 자원을 정리한다.
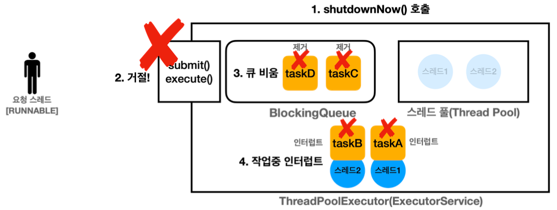
shutdownNow() - 처리중인 작업이 있는 경우
작업 중인 스레드에 인터럽트가 발생하고, 자원을 정리한다.
ExecutorService 우아한 종료 - 구현
shutdown()을 통해 우아한 종료를 시도하고, 10초간 종료되지 않으면shutdownNow()통해 강제 종료하는 방식을 구현해보자.
public class ExecutorShutdownMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
es.execute(new RunnableTask("taskA"));
es.execute(new RunnableTask("taskB"));
es.execute(new RunnableTask("taskC"));
es.execute(new RunnableTask("longTask", 100_000)); // 100초 대기 printState(es);
log("== shutdown 시작 ==");
shutdownAndAwaitTermination(es);
log("== shutdown 완료 ==");
printState(es);
}
static void shutdownAndAwaitTermination(ExecutorService es) {
es.shutdown(); // non-blocking, 새로운 작업을 받지 않는다. 처리 중이거나, 큐에 이미 대기중인 작업은 처리한다.이후에 풀의 스레드를 종료한다.
try {
// 이미 대기중인 작업들을 모두 완료할 때 까지 10초 기다린다. log("서비스 정상 종료 시도"); 블로킹 메서드
if (!es.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
// 정상 종료가 너무 오래 걸리면...
log("서비스 정상 종료 실패 -> 강제 종료 시도");
es.shutdownNow(); // 강제 종료를 하면 작업 중인 스레드에 인터럽트가 발생한다. (로그 확인)
// 작업이 취소될 때 까지 대기한다.
if (!es.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
log("서비스가 종료되지 않았습니다.");
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// awaitTermination()으로 대기중인 현재 스레드가 인터럽트 될 수 있다.
es.shutdownNow();
}
}
}
실행 결과
16:58:30.966 [ main] [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=2, completedTasks=0]
16:58:30.966 [pool-1-thread-1] taskA 시작
16:58:30.966 [pool-1-thread-2] taskB 시작
16:58:30.968 [ main] == shutdown 시작 ==
16:58:30.969 [ main] 서비스 정상 종료 시도
16:58:31.973 [pool-1-thread-2] taskB 완료
16:58:31.973 [pool-1-thread-1] taskA 완료
16:58:31.974 [pool-1-thread-2] taskC 시작
16:58:31.975 [pool-1-thread-1] longTask 시작
16:58:32.977 [pool-1-thread-2] taskC 완료
16:58:40.973 [ main] 서비스 정상 종료 실패 -> 강제 종료 시도
16:58:40.974 [pool-1-thread-1] 인터럽트 발생, sleep interrupted
16:58:40.975 [ main] == shutdown 완료 ==
16:58:40.975 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=4]
//인터럽트에서 예외 발생
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted
at util.ThreadUtils.sleep(ThreadUtils.java:12)
at thread.executor.RunnableTask.run(RunnableTask.java:22)
at java.base/
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1144
)
at java.base/
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:642
)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:1583)
Caused by: java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.sleep0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:509)
at util.ThreadUtils.sleep(ThreadUtils.java:9)
... 4 more
서비스 종료 실패
그런데 마지막에 강제 종료인es.shutdownNow()를 호출한 다음에 왜 10초간 또 기다릴까?shutdownNow()가 작업 중인 스레드에 인터럽트를 호출하는 것은 맞다. 인터럽트를 호출하더라도 여러가지 이유로 작업에 시간이 걸릴 수 있다. 극단적이지만 최악의 경우 스레드가 다음과 같이 인터럽트를 받을 수 없는 코드를 수행중일 수 있다. 이 경우 인터럽트 예외가 발생하지 않고, 스레드도 계속 수행된다.
이런 스레드는 자바를 강제 종료해야 제거할 수 있다. 이런 경우를 대비해서 강제 종료 후 10초간 대기해도 작업이 완료되지 않으면 “서비스가 종료되지 않았습니다”라고 개발자가 인지할 수 있는 로그를 남겨두어야 한다. 그래야 개발자가 나중에 문제를 찾아서 코드를 수정할 수 있다.
while(true) {
// Empty
}
Executor 스레드 풀 관리 - 코드
Executor 프레임워크가 어떤식으로 스레드를 관리하는지 알아본다.
ExecutorService의 기본 구현체인ThreadPoolExecutor의 생성자는 다음 속성을 사용한다.corePoolSize: 스레드 풀에서 관리되는 기본 스레드의 수maximumPoolSize: 스레드 풀에서 관리되는 최대 스레드 수keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit: 기본 스레드 수를 초과해서 만들어진 초과 스레드가 생존할 수 있는 대기 시간, 이 시간 동안 처리할 작업이 없다면 초과 스레드는 제거된다.BlockingQueue workQueue: 작업을 보관할 블로킹 큐
public class ExecutorUtils {
public static void printState(ExecutorService executorService) {
if (executorService instanceof ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor) {
int pool = poolExecutor.getPoolSize();
int active = poolExecutor.getActiveCount();
int queued = poolExecutor.getQueue().size();
long completedTask = poolExecutor.getCompletedTaskCount();
log("[pool=" + pool + ", active=" + active + ", queuedTasks=" + queued + ", completedTasks=" + completedTask + "]");
} else {
log(executorService);
}
}
// 추가(단순히 `taskName` 을 출력하는 부분)
public static void printState(ExecutorService executorService, String taskName) {
if (executorService instanceof ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor) {
int pool = poolExecutor.getPoolSize();
int active = poolExecutor.getActiveCount();
int queued = poolExecutor.getQueue().size();
long completedTask = poolExecutor.getCompletedTaskCount();
log(taskName + " -> [pool=" + pool + ", active=" + active + ", queuedTasks=" + queued + ", completedTasks=" + completedTask + "]");
} else {
log(taskName + " -> " + executorService);
}
}
}
RunnableTask이전에 만든 코드를 사용한다.
public class RunnableTask implements Runnable {
private final String name;
private int sleepMs = 1000;
public RunnableTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public RunnableTask(String name, int sleepMs) {
this.name = name;
this.sleepMs = sleepMs;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log(name + " 시작");
sleep(sleepMs); // 작업 시간 시뮬레이션 log(name + " 완료");
}
}
Main실행
public class PoolSizeMainV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2); // 사이즈를 2로 설정했으므로 최대 2개까지 작업을 큐에 보관할 수 있다.
ExecutorService es = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, workQueue); // 초과 스레드가 생존할 수 있는 대기 시간 3000 밀리초(3초). 3초간 작업을 하지 않고 대기시 제거
printState(es);
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task1"));
printState(es, "task1");
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task2"));
printState(es, "task2");
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task3"));
printState(es, "task3");
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task4"));
printState(es, "task4");
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task5"));
printState(es, "task5");
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task6"));
printState(es, "task6");
try {
es.execute(new RunnableTask("task7"));
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
log("task7 실행 거절 예외 발생: " + e);
}
sleep(3000);
log("== 작업 수행 완료 ==");
printState(es);
sleep(3000);
log("== maximumPoolSize 대기 시간 초과 ==");
printState(es);
es.close();
log("== shutdown 완료 ==");
printState(es);
}
}
실행 결과
11:36:23.260 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0] 11:36:23.263 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
11:36:23.267 [ main] task1 -> [pool=1, active=1, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.267 [ main] task2 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.267 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 시작
11:36:23.267 [ main] task3 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=1, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.268 [ main] task4 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=2, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.268 [ main] task5 -> [pool=3, active=3, queuedTasks=2, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.268 [pool-1-thread-3] task5 시작
11:36:23.268 [ main] task6 -> [pool=4, active=4, queuedTasks=2, completedTasks=0]
11:36:23.268 [pool-1-thread-4] task6 시작
11:36:23.268 [ main] task7 실행 거절 예외 발생: java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task thread.executor.RunnableTask@3abbfa04 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@7f690630[Running, pool size = 4, active threads = 4, queued tasks = 2, completed tasks = 0]
11:36:24.268 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
11:36:24.268 [pool-1-thread-1] task3 시작
11:36:24.269 [pool-1-thread-3] task5 완료
11:36:24.269 [pool-1-thread-3] task4 시작
11:36:24.269 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 완료
11:36:24.269 [pool-1-thread-4] task6 완료
11:36:25.273 [pool-1-thread-1] task3 완료
11:36:25.273 [pool-1-thread-3] task4 완료
11:36:26.273 [ main] == 작업수행완료 ==
11:36:26.273 [ main] [pool=4, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=6]
11:36:29.276 [ main] == maximumPoolSize 대기 시간 초과 ==
11:36:29.277 [ main] [pool=2, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=6]
11:36:29.278 [ main] == shutdown 완료 ==
11:36:29.278 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=6]
Executor 스레드 풀 관리 - 분석
앞에서의 내용을 분석해 본다.
스레드 2개가 작업을 수행하고 있고, 대기큐에 2개의 작업이 쌓이게 된다.
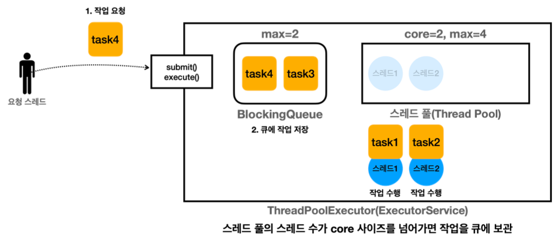
이후 요청되는 작업은 추가 쓰레드가 생성되어 처리 한다.
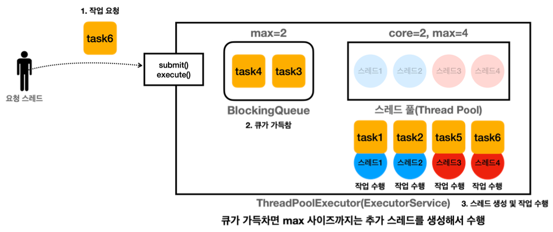
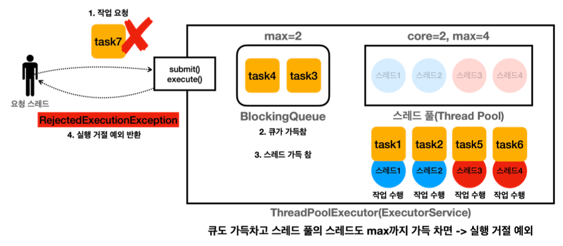
최대 스레드수와 큐를 초과하는 작업은 실행이 거절 된다.
정리
- 작업을 요청하면 core 사이즈 만큼 스레드를 만든다.
- core 사이즈를 초과하면 큐에 작업을 넣는다.
- 큐를 초과하면 max 사이즈 만큼 스레드를 만든다. 임시로 사용되는 초과 스레드가 생성된다.
- 큐가 가득차서 큐에 넣을 수도 없다. 초과 스레드가 바로 수행해야 한다.
- max 사이즈를 초과하면 요청을 거절한다. 예외가 발생한다.
- 큐도 가득차고, 풀에 최대 생성 가능한 스레드 수도 가득 찼다. 작업을 받을 수 없다.
스레드 미리 생성하기
응답시간이 아주 중요한 서버라면, 서버가 고객의 처음 요청을 받기 전에 스레드를 스레드 풀에 미리 생성해두고 싶을 수 있다.(
ThreadPoolExecutor.prestartAllCoreThreads())
public class PrestartPoolMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1000);
printState(es);
ThreadPoolExecutor poolExecutor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) es;
poolExecutor.prestartAllCoreThreads(); // 미리 생성
printState(es);
}
}
로그
12:33:34.971 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTask=0]
12:33:35.117 [ main] [pool=1000, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTask=0]
Executor 전략
ThreadPoolExecutor를 사용하면 스레드 풀에 사용되는 숫자와 블로킹 큐등 다양한 속성을 조절할 수 있다.corePoolSize: 스레드 풀에서 관리되는 기본 스레드의 수maximumPoolSize: 스레드 풀에서 관리되는 최대 스레드 수keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit: 기본 스레드 수를 초과해서 만들어진 스레드가 생존할 수 있는 대기 시간, 이 시간 동안 처리할 작업이 없다면 초과 스레드는 제거된다.BlockingQueue workQueue: 작업을 보관할 블로킹 큐
자바는
Executors클래스를 통해 3가지 기본 전략을 제공한다.
- newSingleThreadPool(): 단일 스레드 풀 전략
- newFixedThreadPool(nThreads): 고정 스레드 풀 전략
- newCachedThreadPool(): 캐시 스레드 풀 전략
Executor 전략 - 고정 풀 전략
- newFixedThreadPool(nThreads)
- 스레드 풀에
nThreads만큼의 기본 스레드를 생성한다. 초과 스레드는 생성하지 않는다. - 큐 사이즈에 제한이 없다. (
LinkedBlockingQueue) - 스레드 수가 고정되어 있기 때문에 CPU, 메모리 리소스가 어느정도 예측 가능한 안정적인 방식이다.
- 스레드 풀에
public class PoolSizeMainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//ExecutorService es = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 2, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
log("pool 생성");
printState(es);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
String taskName = "task" + i;
es.execute(new RunnableTask(taskName));
printState(es, taskName);
}
es.close();
log("== shutdown 완료 ==");
}
}
실행 결과
15:41:31.836 [ main] pool 생성
15:41:31.847 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.849 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
15:41:31.854 [ main] task1 -> [pool=1, active=1, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.854 [ main] task2 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.854 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 시작
15:41:31.854 [ main] task3 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=1, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.854 [ main] task4 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=2, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.854 [ main] task5 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=3, completedTasks=0]
15:41:31.854 [ main] task6 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=4, completedTasks=0]
15:41:32.855 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
15:41:32.856 [pool-1-thread-1] task3 시작
15:41:32.859 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 완료
15:41:32.859 [pool-1-thread-2] task4 시작
15:41:33.860 [pool-1-thread-1] task3 완료
15:41:33.861 [pool-1-thread-1] task5 시작
15:41:33.863 [pool-1-thread-2] task4 완료
15:41:33.863 [pool-1-thread-2] task6 시작
15:41:34.863 [pool-1-thread-2] task6 완료
15:41:34.863 [pool-1-thread-1] task5 완료
15:41:34.864 [ main] == shutdown 완료 ==
- 고정 스레드 전략은 CPU, 메모리 사용량이 예측 가능하고 안정적이다.
- 하지만 스레드 수가 고정되어 있어 사용자나 요청이 늘면 큐에 요청이 쌓이고 지연이 발생함.
- 서버 자원(CPU, 메모리)은 남아있어도 처리 속도가 병목이 되어 응답이 느려지는 문제 발생.
- 특히 사용자 증가나 이벤트성 트래픽 폭증 상황에서 문제가 두드러짐.
Executor 전략 - 캐시 풀 전략
- newCachedThreadPool()
- 기본 스레드를 사용하지 않고, 60초 생존 주기를 가진 초과 스레드만 사용한다. 초과 스레드의 수는 제한이 없다.
- 큐에 작업을 저장하지 않는다. (
SynchronousQueue)- 대신에 생산자의 요청을 스레드 풀의 소비자 스레드가 직접 받아서 바로 처리한다.
- 모든 요청이 대기하지 않고 스레드가 바로바로 처리한다. 따라서 빠른 처리가 가능하다.
new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
SynchronousQueue는 버퍼가 없는 BlockingQueue로, 생산자와 소비자가 1:1로 직접 데이터를 교환하며, 한쪽이 준비될 때까지 다른 쪽은 대기하는 구조다. 즉, 중간 저장 없이 스레드 간 직거래 방식이다.
public class PoolSizeMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// keepAliveTime 60초 -> 3초로 조절. 캐시 스레드 풀 전략은 초과 스레드가 60초의 생존 주기를 가지지만, 여기서는 확인을 위해 3초로 조절
ThreadPoolExecutor es = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>());
log("pool 생성");
printState(es);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
String taskName = "task" + i;
es.execute(new RunnableTask(taskName));
printState(es, taskName);
}
sleep(3000);
log("== 작업 수행 완료 ==");
printState(es);
sleep(3000);
log("== maximumPoolSize 대기 시간 초과 ==");
printState(es);
es.close();
log("== shutdown 완료 ==");
printState(es);
}
}
실행 결과 : 모든 작업이 대기하지 않고 작업의 수 만큼 스레드가 생기면서 바로 실행
16:12:31.681 [ main] pool 생성
16:12:31.690 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
16:12:31.692 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
16:12:31.697 [ main] task1 -> [pool=1, active=1, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
16:12:31.697 [ main] task2 -> [pool=2, active=2, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
16:12:31.697 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 시작
16:12:31.697 [ main] task3 -> [pool=3, active=3, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
16:12:31.697 [pool-1-thread-3] task3 시작
16:12:31.697 [pool-1-thread-4] task4 시작
16:12:31.697 [ main] task4 -> [pool=4, active=4, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=0]
16:12:32.698 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
16:12:32.702 [pool-1-thread-2] task2 완료
16:12:32.702 [pool-1-thread-3] task3 완료
16:12:32.702 [pool-1-thread-4] task4 완료
16:12:34.703 [ main]==작업수행완료==
16:12:34.704 [ main] [pool=4, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=4]
16:12:37.707 [ main] == maximumPoolSize 대기 시간 초과 ==
16:12:37.709 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=4]
16:12:37.710 [ main] == shutdown 완료 ==
16:12:37.710 [ main] [pool=0, active=0, queuedTasks=0, completedTasks=4]
- 특징:
- 기본 스레드 없이 요청 시마다 초과 스레드 생성
SynchronousQueue사용: 큐가 없고 바로 작업 처리- 초과 스레드는 60초 뒤 종료, 유연하게 증감
- 자원을 최대한 활용, 처리 속도 빠름
- 장점:
- 작업량에 따라 스레드 수가 자동 조절
- 유휴 리소스를 활용해 빠르고 유연한 처리 가능
- 단점:
- 무제한 생성되므로, 요청 폭증 시 과도한 스레드로 서버 과부하
- CPU, 메모리 초과 사용 시 시스템 다운 위험
Executor 전략 - 사용자 정의 풀 전략
평소에는 고정된 스레드로 안정적으로 운영하다가, 사용자 요청이 급증하면 일시적으로 스레드를 추가 투입해 빠르게 처리하고, 감당할 수 없는 수준이면 일부 요청은 거절하는 방식을 예시로 만들어 본다.
이를 통해 점진적 사용자 증가와 갑작스러운 요청 폭주 상황 모두에 유연하게 대응할 수 있다.
public class PoolSizeMainV4 {
static final int TASK_SIZE = 1100; // 1. 일반
// static final int TASK_SIZE = 1200; // 2. 긴급
// static final int TASK_SIZE = 1201; // 3. 거절
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService es = new ThreadPoolExecutor(100, 200, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1000));
printState(es);
long startMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 1; i <= TASK_SIZE; i++) {
String taskName = "task" + i;
try {
es.execute(new RunnableTask(taskName));
printState(es, taskName);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
log(taskName + " -> " + e);
}
}
es.close();
long endMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
log("time: " + (endMs - startMs));
}
}
실무에서 자주 하는 실수
LinkedBlockingQueue를 기본 생성자를 통해 무한대의 사이즈로 사용하게 되면, 큐가 가득찰 수 가 없다. 결국 기본 스레드 100개만으로 무한대의 작업을 처리해야 하는 문제가 발생한다. 절대로 스레드 최대 사이즈 만큼 늘어나지 않는다.
new ThreadPoolExecutor(100, 200, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue());
Executor 예외 정책
로그 및 알림을 위한 예외 정책을 만들어 본다.
ThreadPoolExecutor는 작업을 거절하는 다양한 정책을 제공한다.- AbortPolicy: 새로운 작업을 제출할 때
RejectedExecutionException을 발생시킨다. 기본 정책이다. - DiscardPolicy: 새로운 작업을 조용히 버린다.
- CallerRunsPolicy: 새로운 작업을 제출한 스레드가 대신해서 직접 작업을 실행한다.
- 사용자 정의(
RejectedExecutionHandler): 개발자가 직접 정의한 거절 정책을 사용할 수 있다.
- AbortPolicy: 새로운 작업을 제출할 때
AbortPolicy
작업이 거절되면
RejectedExecutionException을 던진다. 기본적으로 설정되어 있는 정책
public class RejectMainV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task1"));
try {
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task2"));
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) { // `AbortPolicy` 는 `RejectedExecutionHandler` 의 구현체
log("요청 초과");
// 포기, 다시 시도 등 다양한 고민을 하면 됨
log(e);
}
executor.close();
}
}
10:08:06.458 [ main] 요청 초과
10:08:06.458 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
10:08:06.460 [ main] java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task java.util.concurrent.FutureTask@79698539[Not completed, task = java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter@79b4d0f[Wrapped task = thread.executor.RunnableTask@6b2fad11]] rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@2f7a2457[Running, pool size = 1, active threads = 1, queued tasks = 0, completed tasks = 0]
10:08:07.466 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
DiscardPolicy
거절된 작업을 무시하고 아무런 예외도 발생시키지 않는다.
public class RejectMainV2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task1"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task2"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task3"));
executor.close();
}
}
실행 결과 :
DiscardPolicy는 조용히 버리는 정책이다.
10:08:25.414 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
10:08:26.422 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
CallerRunsPolicy
호출한 스레드가 직접 작업을 수행하게 한다. 이로 인해 새로운 작업을 제출하는 스레드의 속도가 느려질 수 있다.
public class RejectMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task1"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task2"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task3"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task4"));
executor.close();
}
}
실행 결과 : main 스레드에서 작업을 수행한다. 생산자 스레드가 소비자 대신 일을 수행하는 것도 있지만, 생산자 스레드가 대신 일을 수행하는 덕분 에 작업의 생산 자체가 느려진다
10:08:42.611 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
10:08:42.611 [ main] task2 시작
10:08:43.617 [ main] task2 완료
10:08:43.618 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
10:08:43.619 [ main] task3 시작
10:08:44.625 [ main] task3 완료
10:08:44.626 [pool-1-thread-1] task4 시작
10:08:45.629 [pool-1-thread-1] task4 완료
사용자 정의
사용자는
RejectedExecutionHandler인터페이스를 구현 하여 자신만의 거절 처리 전략을 정의할 수 있다. 이를 통해 특정 요구사항에 맞는 작업 거절 방식을 설정할 수 있다.
거절된 작업을 버리지만, 대신에 경고 로그를 남겨서 개발자가 문제를 인지할 수 있도록 예시를 만들어 보자.
public class RejectMainV4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<>(), new MyRejectedExecutionHandler());
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task1"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task2"));
executor.submit(new RunnableTask("task3"));
executor.close();
}
static class MyRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
int i = count.incrementAndGet();
log("[경고] 거절된 누적 작업 수: " + i);
}
}
}
실행 결과
10:09:03.646 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 시작
10:09:03.646 [ main] [경고] 거절된 누적 작업 수: 1
10:09:03.649 [ main] [경고] 거절된 누적 작업 수: 2
10:09:04.654 [pool-1-thread-1] task1 완료
정리
- 실무 전략 선택
- 고정 스레드 풀 전략: 트래픽이 일정하고, 시스템 안전성이 가장 중요
- 캐시 스레드 풀 전략: 일반적인 성장하는 서비스
- 사용자 정의 풀 전략: 다양한 상황에 대응