[멀티스레드와 동시성] 동기화-synchronized
동시성 문제
공유자원에 동시성 문제가 발생할 수 있는 예제를 만들어 본다.
인터페이스
public interface BankAccount {
boolean withdraw(int amount); // 계좌의 돈을 출금한다.
int getBalance(); // 계좌의 잔액을 반환
}
인터페이스 구현
public class BankAccountV1 implements BankAccount {
private int balance;
//volatile private int balance;
public BankAccountV1(int initialBalance) {
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
@Override
public boolean withdraw(int amount) {
log("거래 시작: " + getClass().getSimpleName());
log("[검증 시작] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
if (balance < amount) {
log("[검증 실패] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
return false;
}
log("[검증 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
sleep(1000); // 출금에 걸리는 시간으로 가정
balance = balance - amount;
log("[출금 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 변경 잔액: " + balance);
log("거래 종료");
return true;
}
@Override
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
출금을 담당하는 Runnable 구현체
public class WithdrawTask implements Runnable {
private BankAccount account;
private int amount;
public WithdrawTask(BankAccount account, int amount) {
this.account = account;
this.amount = amount;
}
@Override
public void run() {
account.withdraw(amount);
}
}
main
public class BankMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount account = new BankAccountV1(1000); // 초기 잔액을 `1000` 원으로 설정
Thread t1 = new Thread(new WithdrawTask(account, 800), "t1"); // `800` 원의 출금
Thread t2 = new Thread(new WithdrawTask(account, 800), "t2"); // `800` 원의 출금
t1.start();
t2.start();
sleep(500); // 검증 완료까지 잠시 대기
log("t1 state: " + t1.getState());
log("t2 state: " + t2.getState());
t1.join();
t2.join();
log("최종 잔액: " + account.getBalance());
}
}
실행 결과
11:09:40.185 [ t1] 거래 시작: BankAccountV1
11:09:40.185 [ t2] 거래 시작: BankAccountV1
11:09:40.192 [ t1] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
11:09:40.192 [ t2] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
11:09:40.192 [ t1] [검증 완료] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
11:09:40.192 [ t2] [검증 완료] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
11:09:40.673 [ main] t1 state: TIMED_WAITING
11:09:40.673 [ main] t2 state: TIMED_WAITING
11:09:41.195 [ t1] [출금 완료] 출금액: 800, 변경 잔액: 200
11:09:41.195 [ t1] 거래 종료
11:09:41.197 [ t2] [출금 완료] 출금액: 800, 변경 잔액: -600
11:09:41.197 [ t2] 거래 종료
11:09:41.200 [ main] 최종 잔액: -600
실행 결과와 같이 모든 스레드가잔고 체크,출금에 걸리는 시간이후에출금이 진행 되어 동시성 문제가 발생한다. 이는volatile을 도입해도 동일하다.
또 완전 동시에 실행되는 상황도 생길 수 있다. 이럴경우최종 잔액은200원이지만출금은1600원이 된다.
임계 영역
critical section여러 스레드가 동시에 접근하면 데이터 불일치나 예상치 못한 동작이 발생할 수 있는 위험하고 또 중요한 코드 부분을 뜻한다.
여러 스레드가 동시에 접근해서는 안 되는 공유 자원을 접근하거나 수정하는 부분을 의미한다.
예제의withdraw(int amount)메서드의잔액( balance )을 검증하는 단계부터잔액의 계산을 완료할 때 까지가 임계 영역이다.
synchronized 메서드
자바의 synchronized 키워드를 사용하면 한 번에 하나의 스레드만 실행할 수 있는 코드 구간을 만들 수 있다.
public class BankAccountV2 implements BankAccount {
private int balance;
public BankAccountV2(int initialBalance) {
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
@Override
public synchronized boolean withdraw(int amount) {
log("거래 시작: " + getClass().getSimpleName());
log("[검증 시작] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
if (balance < amount) {
log("[검증 실패] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
return false;
}
log("[검증 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
sleep(1000);
balance = balance - amount;
log("[출금 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 변경 잔액: " + balance);
log("거래 종료");
return true;
}
@Override
public synchronized int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
synchronized 코드 블럭
자바의 synchronized 키워드를 사용하면 한 번에 하나의 스레드만 실행할 수 있는 코드 구간을 만들 수 있다.
public class BankAccountV2 implements BankAccount {
private int balance;
public BankAccountV2(int initialBalance) {
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
@Override
public synchronized boolean withdraw(int amount) { // synchronized 추가!!
log("거래 시작: " + getClass().getSimpleName());
log("[검증 시작] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
if (balance < amount) {
log("[검증 실패] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
return false;
}
log("[검증 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
sleep(1000);
balance = balance - amount;
log("[출금 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 변경 잔액: " + balance);
log("거래 종료");
return true;
}
@Override
public synchronized int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
BankMain 에서 BankAccountV2 를 실행하도록 코드를 변경하고 실행해 보자.
public class BankMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//BankAccount account = new BankAccountV1(1000);
BankAccount account = new BankAccountV2(1000);
...
}
}
실행 결과
14:48:15.144 [ t1] 거래 시작: BankAccountV2
14:48:15.149 [ t1] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
14:48:15.149 [ t1] [검증 완료] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
14:48:15.633 [ main] t1 state: TIMED_WAITING
14:48:15.633 [ main] t2 state: BLOCKED
14:48:16.155 [ t1] [출금 완료] 출금액: 800, 변경 잔액: 200
14:48:16.155 [ t1] 거래 종료
14:48:16.156 [ t2] 거래 시작: BankAccountV2
14:48:16.156 [ t2] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 200
14:48:16.156 [ t2] [검증 실패] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 200
14:48:16.160 [ main] 최종 잔액: 200
synchronized 분석
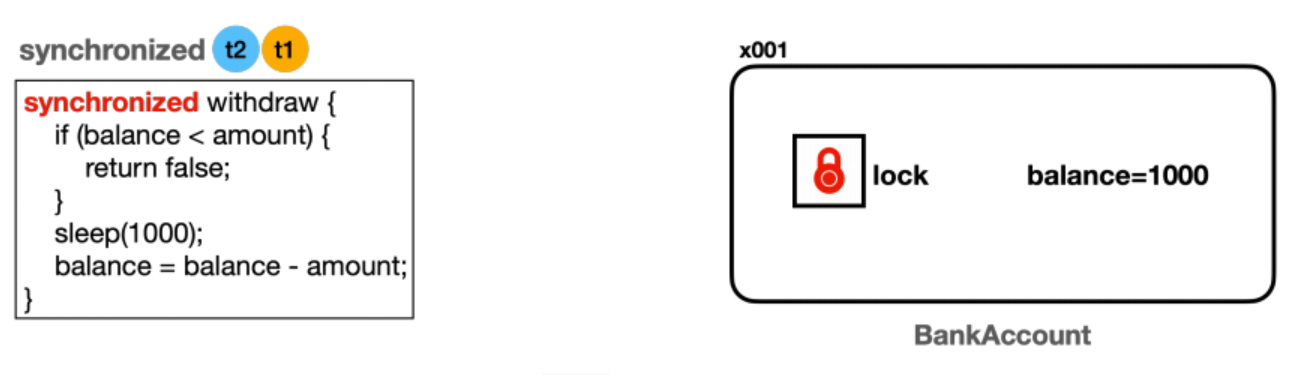
- 모든 객체(인스턴스)는 내부에 자신만의 락(
lock)을 가지고 있다. - 스레드가
synchronized키워드가 있는 메서드에 진입하려면 반드시 해당 인스턴스의 락이 있어야 한다! BankAccount(x001)인스턴스의synchronized withdraw()메서드를 호출하므로 이 인스턴스의 락이 필요하다.
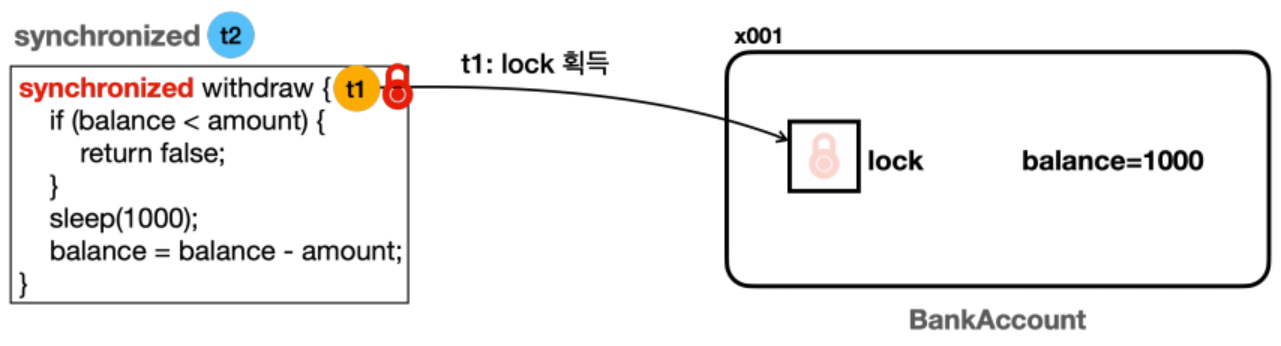
- 스레드
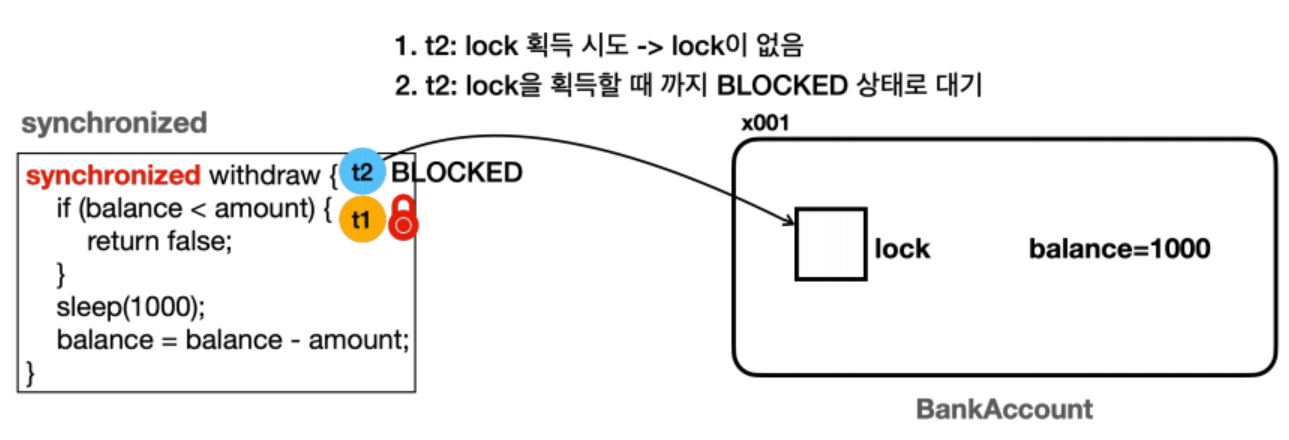
t2도withdraw()메서드 호출을 시도한다.synchronized메서드를 호출하려면 먼저 해당 인스턴스의 락이 필요하다. - 스레드
t2는BankAccount(x001)인스턴스에 있는 락 획득을 시도한다. 하지만 락이 없다. 이렇게 락이 없으면t2스레드는 락을 획득할 때 까지BLOCKED상태로 대기한다.t2스레드의 상태는RUNNABLE>BLOCKED상태로 변하고, 락을 획득할 때 까지 무한정 대기한다.
t1메서드 호출이 끝나면 락을 반납한다.- 인스턴스에 락이 반납되면 락 획득을 대기하는 스레드는 자동으로 락을 획득한다.
- 이때 락을 획득한 스레드는
BLOCKED>RUNNABLE상태가 되고, 다시 코드를 실행한다.
- 이때 락을 획득한 스레드는
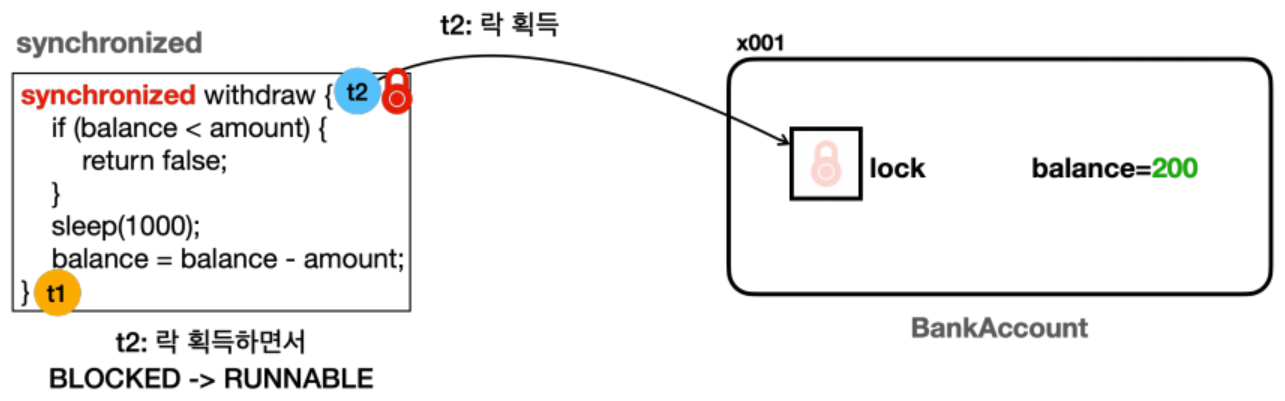
t2는 출금을 위한 검증 로직을 수행한다. 조건을 만족하지 않으므로false를 반환하고, 락을 반납하면서return한다.
참고: 락을 획득하는 순서는 보장되지 않는다.
synchronized 코드 블럭
synchronized는 기본적으로 메서드 단위로 적용되기 때문에 성능 저하가 발생할 수 있다. 자바에서는 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해코드 블록단위로 필요한 부분에만synchronized를 적용할 수 있는 기능을 제공한다.
public class BankAccountV3 implements BankAccount {
private int balance;
public BankAccountV3(int initialBalance) {
this.balance = initialBalance;
}
@Override
public boolean withdraw(int amount) {
log("거래 시작: " + getClass().getSimpleName());
synchronized (this) { // 안전한 임계 영역을 코드 블럭으로 지정한다.
log("[검증 시작] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
if (balance < amount) {
log("[검증 실패] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
return false;
}
log("[검증 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 잔액: " + balance);
sleep(1000);
balance = balance - amount;
log("[출금 완료] 출금액: " + amount + ", 변경 잔액: " + balance);
}
log("거래 종료");
return true;
}
@Override
public synchronized int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
실행 결과
14:20:51.851 [ t1] 거래 시작: BankAccountV3
14:20:51.851 [ t2] 거래 시작: BankAccountV3
14:20:51.858 [ t1] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
14:20:51.858 [ t1] [검증 완료] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 1000
14:20:52.337 [ main] t1 state: TIMED_WAITING
14:20:52.337 [ main] t2 state: BLOCKED
14:20:52.861 [ t1] [출금 완료] 출금액: 800, 변경 잔액: 200
14:20:52.862 [ t1] 거래 종료
14:20:52.862 [ t2] [검증 시작] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 200
14:20:52.864 [ t2] [검증 실패] 출금액: 800, 잔액: 200
14:20:52.869 [ main] 최종 잔액: 200
문제와 풀이
문제1 - 공유 자원
- 다음 코드의 결과는
20000이 되어야 한다. - 이 코드의 문제점을 찾아서 해결해라.
- 이 코드에서 다른 부분은 변경하면 안되고,
Counter클래스 내부만 수정해야 한다.
public class SyncTest1BadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
counter.increment();
}
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("결과: " + counter.getCount());
}
static class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void increment() {
count = count + 1;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
}
정답
static class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
count = count + 1;
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
문제2 - 지역 변수의 공유
- 다음 코드에서
MyTask의run()메서드는 두 스레드에서 동시에 실행한다. - 다음 코드의 실행 결과를 예측해보자.
- 그리고
localValue지역 변수에 동시성 문제가 발생하는지 하지 않는지 생각해보자.
public class SyncTest2Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyCounter myCounter = new MyCounter();
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
myCounter.count();
}
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task, "Thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task, "Thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
static class MyCounter {
public void count() {
int localValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
localValue = localValue + 1;
}
log("결과: " + localValue);
}
}
}
localValue는 지역 변수이므로 동시성 문제가 발생하지 않는다. 지역 변수는 각 스레드의스택 영역에 별도의 메모리 공간이 할당되기 때문에 다른 스레드와 공유되지 않는다.
문제3 - final 필드
다음에서 value 필드(멤버 변수)는 공유되는 값이다. 멀티스레드 상황에서 문제가 될 수 있을까?
class Immutable {
private final int value;
public Immutable(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
}
필드에 final 이 붙으면 어떤 스레드도 값을 변경할 수 없다. 따라서 멀티스레드 상황에 문제 없는 안전한 공유 자원이 된다. 여러 스레드가 접근 가능한 공유 자원이라도 그 값을 아무도 변경할 수 없다면 문제 되지 않는다.